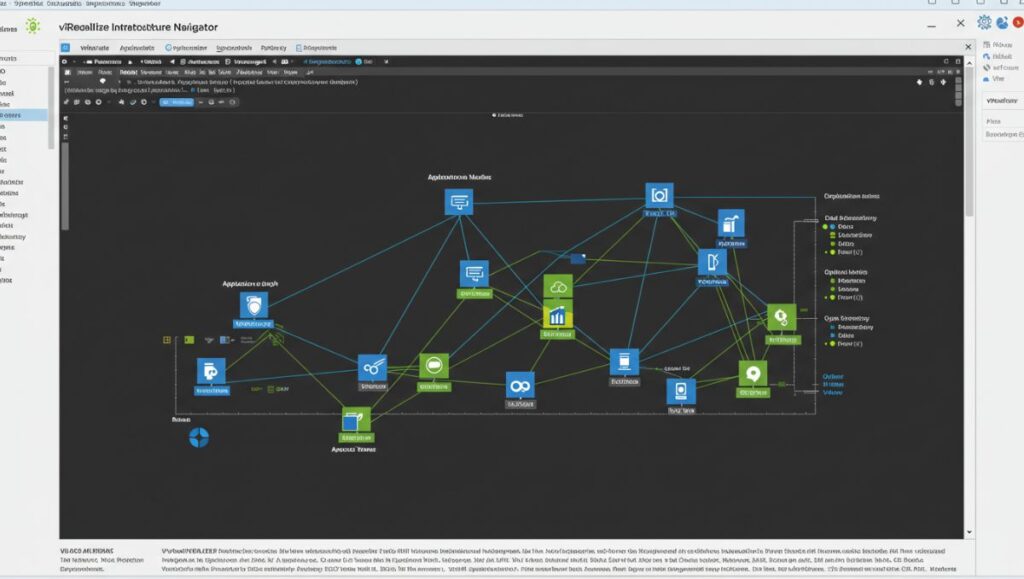
As data centers grow more complex, understanding how applications interact within a virtual infrastructure becomes critical for IT operations, security, and business continuity. VMware’s vRealize Infrastructure Navigator (VIN) was developed to tackle this challenge—offering visibility into application dependencies across virtual machines (VMs) hosted in VMware vSphere environments.
In this article, we explore what vRealize Infrastructure Navigator is, how it works, key features, its benefits, use cases, and why application dependency mapping is vital in today’s hybrid IT environments.
What is vRealize Infrastructure Navigator?
vRealize Infrastructure Navigator (VIN) was a component of the VMware vRealize Suite, designed to automatically discover applications running inside virtual machines and map out their interdependencies. By providing real-time visibility into these connections, administrators could better manage, plan, and secure their VMware environments.
VIN is integrated directly into vCenter Server and displays application topologies and dependencies within the vSphere Web Client, giving IT teams insight into how software components interact across VMs, clusters, or data centers.
Note: As of recent updates, VIN has been deprecated and replaced by more advanced tools like VMware Aria Operations for Applications (formerly Tanzu Observability) and vRealize Network Insight.
Key Features of vRealize Infrastructure Navigator
1. Automated Application Discovery
VIN automatically scans VMs to identify:
-
Installed operating systems
-
Application types (e.g., database servers, web servers)
-
Specific services and ports
-
Middleware and enterprise software
This scanning process uses VMware Tools for guest OS introspection and leverages fingerprinting techniques to identify applications without needing in-guest agents.
2. Application Dependency Mapping
VIN visualizes inbound and outbound network connections between virtual machines, giving administrators a clear view of:
-
Multi-tier applications (e.g., front-end, app, and database layers)
-
Service dependencies
-
Application flows across networks and clusters
This data is presented through interactive topology maps embedded in the vSphere interface.
3. Change Detection and Real-Time Updates
VIN detects changes to the application infrastructure in near real-time. If a new application is installed or a service starts communicating with a new endpoint, the dependency map updates accordingly.
4. Seamless Integration with vSphere
Since VIN was natively integrated into vCenter Server and the vSphere Web Client, it required minimal setup and followed the existing VMware administrative workflows.
How vRealize Infrastructure Navigator Works
System Architecture
-
VIN Appliance: A virtual machine that connects to vCenter Server
-
VMware Tools: Required on guest operating systems for application discovery
-
vSphere Web Client Plugin: Displays application maps and dependencies in the UI
Discovery Process
-
VIN scans all VMs managed by vCenter.
-
Using VMware Tools, it collects metadata about OS, services, and open ports.
-
VIN correlates this data to determine which applications are running and how they communicate with other VMs.
-
Dependency relationships are mapped and visualized through the vSphere interface.
Benefits of vRealize Infrastructure Navigator
Enhanced Visibility
Knowing which services rely on one another helps prevent unintended disruptions during maintenance, migration, or upgrades. VIN ensures you understand the full impact of changes before taking action.
Improved Change Management
With VIN’s dependency data, IT teams can design better change control processes, ensuring that critical services aren’t accidentally taken offline during infrastructure modifications.
Risk Reduction for Migrations
During cloud migrations or data center consolidation, knowing how VMs are interconnected is crucial. VIN simplifies pre-migration assessments by revealing application ties and hidden dependencies.
Faster Troubleshooting
When performance issues occur, VIN allows admins to trace dependencies between applications and isolate the cause of disruptions—whether it’s a network failure, database slowdown, or VM misconfiguration.
Better Compliance and Auditing
VIN’s discovery and mapping features can assist with compliance efforts (e.g., PCI-DSS, HIPAA) by documenting where sensitive applications reside and how they interact.
Common Use Cases
1. Data Center Modernization
Organizations moving from legacy environments to software-defined data centers (SDDC) use VIN to understand current application architectures before implementing major changes.
2. Disaster Recovery Planning
VIN helps in defining recovery groups by identifying which applications and VMs need to be recovered together to maintain business continuity.
3. Security Hardening
Mapping application communication helps security teams identify unauthorized services or unnecessary open ports, reducing potential attack surfaces.
4. Application Performance Optimization
VIN can uncover inefficient routing or bottlenecks in multi-tier applications, enabling performance tuning.
Limitations of vRealize Infrastructure Navigator
While VIN provided significant advantages, it had limitations:
-
Support only for VMware environments (no visibility into physical or multi-cloud workloads)
-
Dependent on VMware Tools, which had to be installed and running in all guest OSes
-
No machine learning or advanced analytics—VIN provided raw topology, but not predictive insight
-
Limited OS and application support—though broad, it did not recognize all third-party services or custom applications
These limitations eventually led to its deprecation in favor of more modern and scalable tools.
Modern Alternatives to VIN
With VMware’s shift toward hybrid cloud, microservices, and Kubernetes, more advanced tools have replaced VIN:
vRealize Network Insight (now part of VMware Aria Suite)
-
Deep visibility into network flows, security groups, and application behavior
-
Support for multi-cloud environments, including AWS and Azure
-
Integration with NSX-T and physical network infrastructure
-
ML-based traffic pattern analysis
VMware Aria Operations for Applications
-
Full-stack observability for apps, infrastructure, and services
-
Real-time analytics with dashboards, alerts, and anomaly detection
-
Ideal for cloud-native and containerized environments
These platforms offer more scalability, better data correlation, and multi-cloud intelligence, making them ideal replacements for VIN.
Final Thoughts
vRealize Infrastructure Navigator was a pioneering tool that brought much-needed transparency to virtualized application infrastructures. It served as a bridge between traditional VM management and application-centric operations.
However, as enterprise IT evolves toward cloud-native, containerized, and distributed architectures, VIN’s capabilities are now largely outdated. VMware’s newer platforms—like Aria Operations, Aria Graph, and vRealize Network Insight—offer deeper insights, broader compatibility, and AI-driven analytics.
If you’re still running a legacy vSphere environment and need a quick, visual map of application dependencies, VIN may still be useful. But for modern IT operations, upgrading to Aria Suite components is the future-forward strategy.