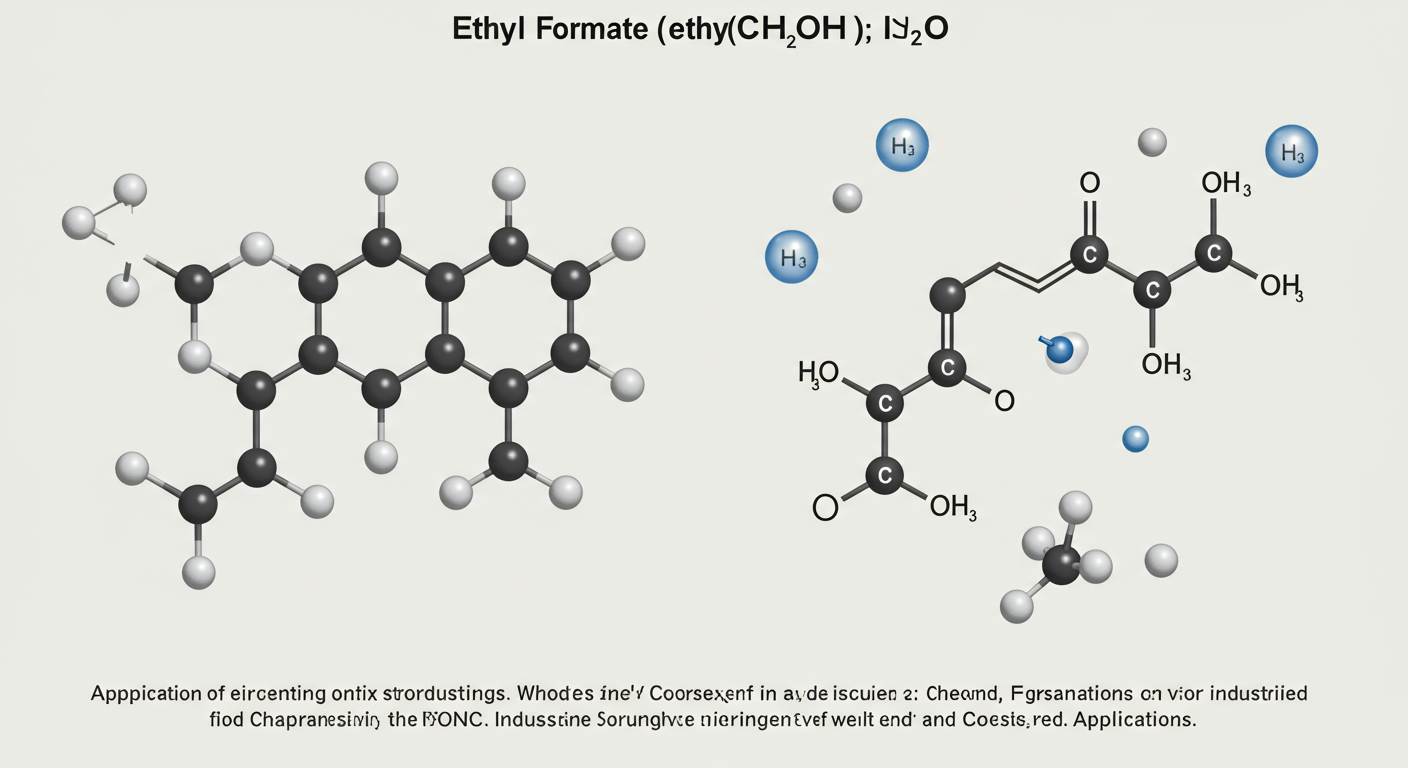
Chemistry often uses formulas and molecular structures to represent complex compounds. One such notation is HCOOCH CH2 H2O, which may appear confusing at first glance but carries significance in understanding organic reactions and functional groups. This formula is likely a shorthand or combined notation for a formate-related compound interacting with a hydroxymethyl group and water.
In this article, we will break down what HCOOCH CH2 H2O represents, its chemical meaning, possible reactions, and real-world relevance in organic synthesis and industry.
Breaking Down the Formula HCOOCH CH2 H2O
To understand the formula, let’s examine its parts:
-
HCOO– → represents the formate group, derived from formic acid (HCOOH).
-
CH2– → indicates a methylene group, common in organic structures.
-
H2O → represents water, often associated with hydration or solvent conditions.
When combined, HCOOCH CH2 H2O suggests a relationship between a formate ester, a methylene group, and water—possibly an intermediate or hydrated compound in organic chemistry.
Possible Interpretations of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
-
Formate Ester Hydrate
-
The formula could represent a formic acid ester (HCOOR type) with hydration.
-
Example: Methyl formate (HCOOCH3) interacting with water.
-
-
Intermediate in Organic Reactions
-
Could occur during esterification or hydrolysis.
-
The CH2 group may link to alcohol or aldehyde functionality.
-
-
Simplified Notation
-
In some texts, chemists use shorthand formulas for ease, and HCOOCH CH2 may be a compact way to denote a hydrated organic molecule.
-
HCOOCH CH2 H2O in Organic Chemistry
1. Esterification and Hydrolysis
-
Formate esters (like methyl formate or ethyl formate) can interact with water (H2O).
-
Hydrolysis of esters regenerates formic acid + alcohol.
-
Example reaction:
HCOOCH3+H2O→HCOOH+CH3OHHCOOCH_3 + H_2O → HCOOH + CH_3OH
-
A similar process could be represented with HCOOCH CH2.
2. Role in Aldehyde Chemistry
-
The CH2 group may indicate aldehyde linkage (–CH2OH).
-
Hydration can stabilize aldehydes in aqueous solutions.
3. Functional Group Analysis
-
Formates are key intermediates in fuel cells, solvents, and organic synthesis.
-
When combined with CH2 and water, they may represent transitional or reactive forms.
Industrial Relevance of HCOOCH CH2
1. Solvent Applications
-
Formates are lightweight, volatile esters used in perfumes, solvents, and cleaning agents.
-
Hydration impacts their stability and usability.
2. Energy and Fuel Research
-
Formate salts and esters are being studied as hydrogen storage materials.
-
The combination with water (H2O) is essential for hydrogen release in fuel cells.
3. Pharmaceutical Chemistry
-
Formate groups appear in drug intermediates.
-
CH2 linkages allow modification of molecular activity.
-
Water (hydration) influences solubility and delivery.
Properties of Compounds Related to HCOOCH CH2 H2O
-
Molecular Weight: Depends on exact structure (if methyl/ethyl group included).
-
State: Likely a liquid at room temperature (esters are often volatile).
-
Solubility: Moderately soluble in water due to ester + formate interactions.
-
Odor: Formate esters usually have a fruity odor, used in fragrances.
Laboratory Considerations
-
Synthesis
-
Produced by reacting formic acid with alcohols.
-
Presence of water (H2O) affects equilibrium.
-
-
Stability
-
Formates can hydrolyze in aqueous conditions.
-
CH2 group linkages may oxidize under strong conditions.
-
-
Storage
-
Should be stored away from moisture to prevent decomposition.
-
Environmental Impact
-
Biodegradability – Formates and related compounds break down naturally.
-
Eco-Friendly Solvents – Some esters based on formates are marketed as greener alternatives.
-
Water Interaction – Hydrated forms (as in HCOOCH CH2 H2O) are less volatile and may be safer.
Future Research on HCOOCH CH2 H2O
-
Green Chemistry – Developing safer esters with hydration stability.
-
Renewable Fuels – Using formate-water chemistry for hydrogen generation.
-
Biological Pathways – Investigating formate and aldehyde roles in metabolism.
The study of compounds like HCOOCH CH2 shows how small structural differences influence stability, reactivity, and usability in various fields.
Conclusion
The formula HCOOCH CH2 H2O points to a compound related to formate esters, methylene groups, and hydration. Though not a standard IUPAC representation, it highlights important concepts in organic chemistry, energy research, and industrial applications.
From esterification and hydrolysis to renewable fuel applications, compounds like this underscore the link between structure and function in chemistry. As green chemistry and renewable energy continue to grow, the role of hydrated formates and related compounds will become increasingly significant.